Network drives
ST-DOS has an experimental implementation of network drives. With network drives you can easily access files that are
stored in another computer, for example a Linux or another ST-DOS machine.
The client program is an ST-DOS device driver that interpretes the read and write calls from the kernel to the server,
and brings the answer from the server back to the kernel. The server program is a simple C program that compiles to both
ST-DOS and POSIX compliant operating systems.
Download client
Download server
How to use
Config files
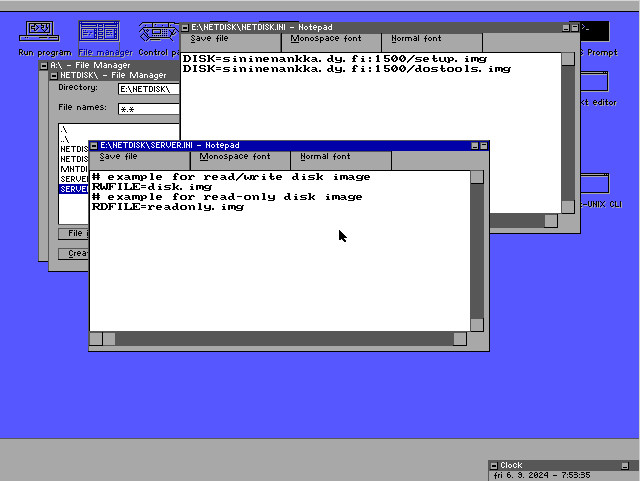
The client-side config file has one attribute: DISK. An example of the client's config file looks like this:
DISK=sininenankka.dy.fi:1500/setup.img DISK=sininenankka.dy.fi:1500/dostools.img
The format is [dns|ip address]:[port]/[filename].
The server-side config file has two attributes, RDFILE and RWFILE. RDFILE is used to specify a read-only disk, and
RWFILE specifies a read-write disk. An example row of server's config file looks like this:
RDFILE=readonly.img RWFILE=readwrit.img
The maximum length of a filename is 8+3 characters. On ST-DOS you can also share locally mounted filesystems (DRV:n) and device files. The server program also works on FreeDOS (and probably on all other DOS implementations), but is only able to share filesystem images.
Mounting remote filesystems
After NETDISK.EXE has been successfully loaded with a properly made config file, a device file is created for every network disk. The names of those device files start with ND. Those are just raw device files and you need to tell the kernel what filesystem type they have and what mount point to use for them. This example command mounts a device file ND0 to the mount point B:, when ND0 has a FAT12 filesystem:
MOUNT ND0 B: 1
Sharing filesystems
The config file and the shared filesystem images (or symbolic links to them) must be in the same directory as the server program binary. By default the server listens to UDP port 300, but you can specify a different port as a command line argument.
Step-to-step instructions
1. Download DOSTOOLS.IMG. Write it to a diskette or save it to a ISO9660 CD-ROM disk or other media that ST-DOS can read. This is the easiest way to transfer the necessary files to ST-DOS.
1.5 If you saved the disk image to a CD-ROM disk, you need to mount it using the MOUNT command:
MOUNT DOSTOOLS.IMG B: 1
2. Navigate to the drive, select the NETDISK directory and press the [COPY] button.
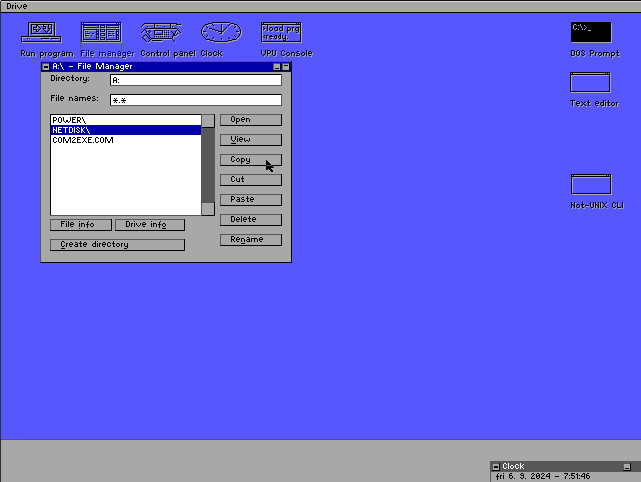
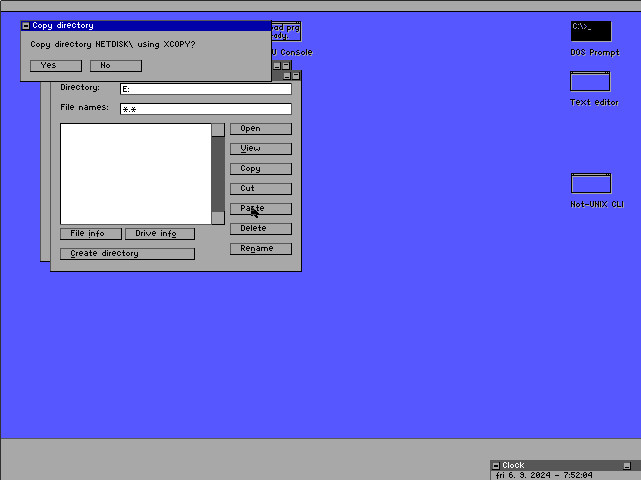
3. Navigate to the target directory and press the [PASTE] button. Select [YES] and let XCOPY do its thing.
4. Configure the client and/or server programs using their respective .INI files. The easiest way to edit these
files is using the Notepad program. Press the [View] button in the File Manager to open a file in Notepad. The default
configuration of the client program connects to two remote disks, which are the 1,44 MB setup disk of ST-DOS and the DOSTOOLS disk that
can be downloaded from this page.
5. Sharing filesystems is easy: Just configure the server program and run it. Pressing CTRL+BREAK exits the
program. Setting up the client side requires one extra step: Mounting the device file.
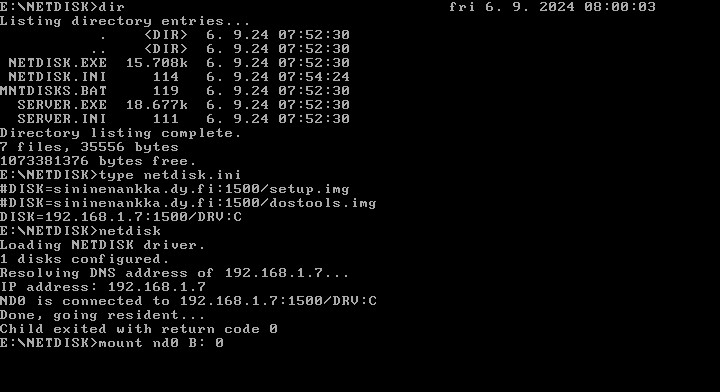
In this case the file DRV:C (the C: drive) is shared by the remote computer and accessed by the local machine. The
filesystem type is 0 (FAT16).
The files on the remote computer can be accessed with the local machine as if they were local files.